Hemorrhagic Stroke
There are two types of stroke, hemorrhagic and ischemic. Hemorrhagic strokes are less common, in fact only 15 percent of all strokes are hemorrhagic, but they are responsible for about 40 percent of all stroke deaths.
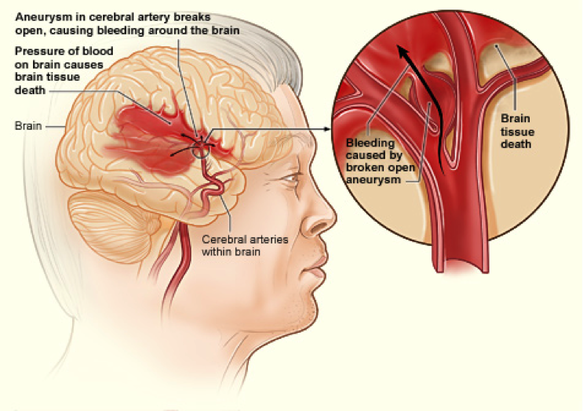
A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts and spills blood into or around the brain. High blood pressure and aneurysm (a weak or thin spot on a blood vessel wall) can make blood vessels weak enough to burst. Blood spills into or around the brain and creates swelling and pressure, damaging cells and tissue in the brain. There are two types of hemorrhagic stroke: subarachnoid and intracerebral.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: In a subarachnoid hemorrhage, an aneurysm bursts in a large artery on or near the thin, delicate membrane surrounding the brain. Blood spills into the area around the brain, which is filled with a protective fluid, causing the brain to be surrounded by blood-contaminated fluid.
This type of stroke involves bleeding in the area between the brain and the tissue covering the brain, known as the subarachnoid space. This type of stroke is most often caused by a burst aneurism. Other causes include:
Sometimes intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke can be caused by an arteriovenous malformation (AVM). AVM is a genetic condition of abnormal connection between arteries and veins and most often occurs in the brain or spine. If AVM occurs in the brain, vessels can break and bleed into the brain. The cause of AVM is unclear but once diagnosed it can be treated successfully.
A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts and spills blood into or around the brain. High blood pressure and aneurysm (a weak or thin spot on a blood vessel wall) can make blood vessels weak enough to burst. Blood spills into or around the brain and creates swelling and pressure, damaging cells and tissue in the brain. There are two types of hemorrhagic stroke: subarachnoid and intracerebral.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: In a subarachnoid hemorrhage, an aneurysm bursts in a large artery on or near the thin, delicate membrane surrounding the brain. Blood spills into the area around the brain, which is filled with a protective fluid, causing the brain to be surrounded by blood-contaminated fluid.
This type of stroke involves bleeding in the area between the brain and the tissue covering the brain, known as the subarachnoid space. This type of stroke is most often caused by a burst aneurism. Other causes include:
- AVM
- Bleeding disorders
- Head injury
- Blood thinners
Sometimes intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke can be caused by an arteriovenous malformation (AVM). AVM is a genetic condition of abnormal connection between arteries and veins and most often occurs in the brain or spine. If AVM occurs in the brain, vessels can break and bleed into the brain. The cause of AVM is unclear but once diagnosed it can be treated successfully.
| explainingstrokebrochure.pdf | |
| File Size: | 1596 kb |
| File Type: | |
| nsafactsheet_socialsupport_2014.pdf | |
| File Size: | 178 kb |
| File Type: | |
| nsafactsheet_managinglifeathome_2014.pdf | |
| File Size: | 211 kb |
| File Type: | |
New Breakthrough in Hemorrhagic Stroke Treatment
When someone has a hemorrhagic stroke, blood from a burst blood vessel leaks out into the brain. The leaked blood is harmful to the surrounding brain tissue and needs to be removed.
What is the new treatment?
What is the new treatment?