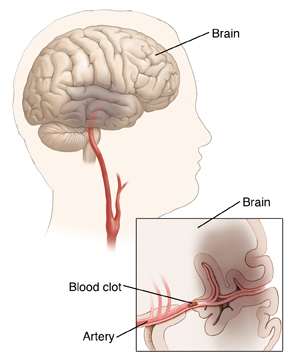
Restoring normal blood flow can limit damage to brain tissue and improve outcome. With thrombolytic therapy, a clot-busting medicine called tissue plasminogen activator or tPA) is used to dissolve the clot.
It is very important that you go to the hospital immediately, if you or someone else is having a stroke or had one. The clot busting medication works well if you get to the hospital FAST...meaning as soon as you think you or someone else had a stroke. Right then, immediately.
You cannot go to sleep and say "Let's see how I feel when I wake up." Do not try home remedy first! Go to the hospital IMMEDIATELY, otherwise this medicine will not work if you have a clot and a stroke for more than a few short hours.
If you are at work, tell your supervisor you have a stroke and get to the hospital ASAP...within that first few hours. Getting rid of that clot means the difference between life and death or decreased quality of life with disability.
Before the treatment
- People with certain health problems have increased risks of problems with thrombolytic therapy. For this reason, a detailed health history must be taken to check whether it is safe to have the treatment. Be sure to tell your health care provider about any health problems you have. The provider will also ask whether you’ve had specific problems, such as a prior stroke, head injury, and bleeding in the brain.
- Tell the health care provider about all medicines you take. Be sure to mention if you take blood thinners (anticoagulants). Also mention if you take over-the-counter drugs, herbal medicines, and other supplements.
- Tell your health care provider about the use of any alcohol or tobacco products so that he or she can provide you with the safest possible care.
- Tell your health care provider if you are pregnant or if you have had recent surgery or head injury.
- Certain tests need to be done before the treatment. These include blood tests and imaging tests, such as a CT or MRI scan of the brain. The imaging test helps to tell what kind of stroke you have. Remember that not everyone can get the clot busting drug.
During the treatment
The treatment is done using an IV line. This is a small tube that is put in a vein in the hand or arm. Clot-busting medicine is sent through the IV line to reach the clot. The medicine is delivered continuously for one or more hours. You’ll be monitored closely throughout the treatment.
After the treatment
Following the treatment, you’ll need to stay in the hospital for several days or longer. More imaging tests will be done to check how well the clot is dissolving. Other tests may also be done to help find the cause of the stroke.
Risks and complications
Risks and complications include:
· Bleeding in the brain or elsewhere in the body
· Allergic reaction to the clot-busting medication (skin rash, itching, swelling of your face or tongue)
· Chest pain or pressure
· Severe headache
· Shortness of breath
· Worsening of heart problems
· Dizziness or lightheadedness
· Nausea and vomiting
· Death
Follow-up care
Recovery from a stroke can take several months or longer. Be sure to keep all follow-up appointments with your doctor. These are needed to monitor your health and the progress of your recovery. Other treatments, such as medicines, rehabilitation, and surgery, may be needed in the future. Your health care provider will discuss these with you as needed.
When to seek emergency care
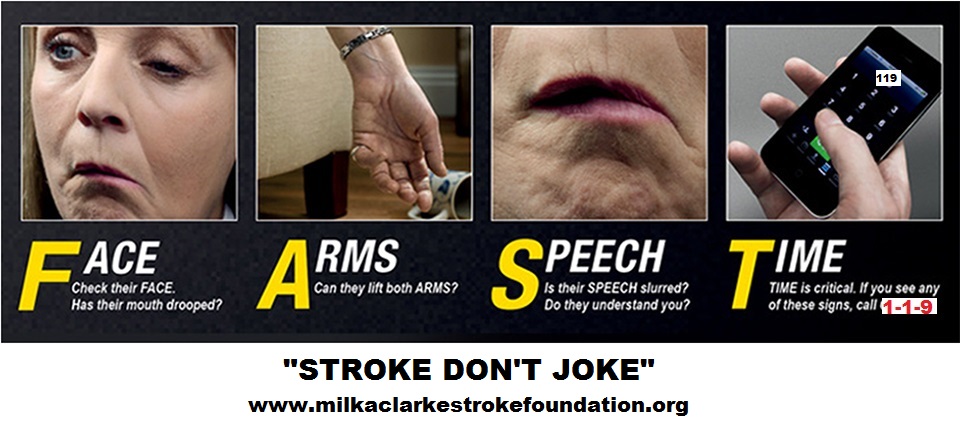
Call 119 or go to an emergency department (ED) right away if you have any of the following signs of a stroke:
· Sudden, unexplained numbness or weakness on one side of the body
· Problems seeing, double vision, or blurry vision
· Sudden confusion or problems with speech
· Sudden dizziness, trouble walking, or problems with balance
· Sudden, severe headache
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed